Network+ Guide to Networks Review Questions Answers Chapter 1
Instructor Planning Guide
Activities
What activities are associated with this chapter?

Assessment
Students should complete Chapter ane, "Assessment" after completing Affiliate 1.
Quizzes, labs, Parcel Tracers and other activities can be used to informally appraise student progress.
Introduction to Networks
1.1 Globally Connected
Explain how multiple networks are used in every solar day life.
Explain how networks affect the way nosotros interact, learn, work and play.
Explicate how host devices tin can be used as clients, servers, or both.
1.2 LANs, WANs, and the Internet
Explain how topologies and devices are connected in a small to medium-sized business organization network.
Explain the use of network devices..
Compare the devices and topologies of a LAN to the devices and topologies of a WAN.
Depict the basic structure of the Cyberspace.
Explain how LANs and WANs interconnect to the Internet.
1.iii The Network as a Platform
Explain the basic characteristics of a network that supports communication in a modest to medium-sized business.
Explain the concept of a converged network.
Draw the four basic requirements of a reliable network.
1.4 The Changing Network Environment
Explicate trends in networking that will touch the use of networks in small to medium-sized businesses.
Explain how trends such as BYOD, online collaboration, video, and cloud calculating are changing the style nosotros interact.
Explain how networking technologies are irresolute the abode environment.
Identify some basic security threats and solutions for both small and large networks.
Explain why information technology is important to understand the switching and routing infrastructure of a network.
Explore the Network
1.i Globally Connected
1.1.1 Networking Today
ane.1.ane.one Networks in Our Daily Lives
Welcome to a earth where we are more powerful together, than we ever could be autonomously.
Welcome to the human network.

ane.1.one.2 Technology Then and Now
Nosotros alive in a earth we barely imagined twenty years ago.
What wouldn't we have without the Internet?
What volition be possible in the hereafter using the network as the platform?


one.1.ane.3 No Boundaries
Advancements in networking technologies are helping create a world without boundaries.
The immediate nature of communications over the Internet encourages global communities.
Cisco refers to the impact of the Internet and networks on people the "human network".

1.1.i.four Networks Support the Manner We Learn
Do you remember sitting in a classroom, like this?
You don't accept to be in schoolhouse anymore to have a grade. Yous don't accept to be in a classroom to have a teacher.


one.1.1.5 Networks Support the Way Nosotros Work
The globalization of the Internet has empowered individuals to create information that can be accessed globally.
Forms of communication:
♦ Texting
♦ Social Media
♦ Collaboration Tools
♦ Blogs
♦ Wikis
♦ Podcasting

Data networks have evolved into helping back up the way we piece of work.
Online learning opportunities decrease costly and time consuming travel.
Employee training is becoming more cost effective.

1.one.one.six Networks Support the Style We Play
We mind to music, watch movies, read books, and download fabric for future offline admission.
Networks allow online gaming in ways that were not possible 20 years ago.
Offline activities have also been enhanced past networks including global communities for a wide range of hobbies and interests.
How do y'all play on the Internet?

1.ane.1.7 – Lab – Researching Network Collaboration Tools

1.1.2– Providing Resources in a Network
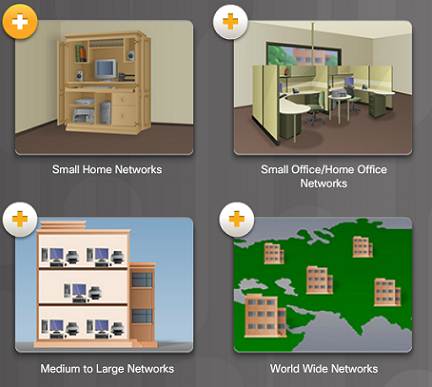
1.1.2.1 – Networks of Many Sizes
Small-scale Home Networks – connect a few computers to each other and the Internet
Small Office/Home Office – enables computer within a dwelling house or remote office to connect to a corporate network
Medium to Large Networks – many locations with hundreds or thousands of interconnected computers
Globe Wide Networks – connects hundreds of millions of computers world-wide – such equally the Internet
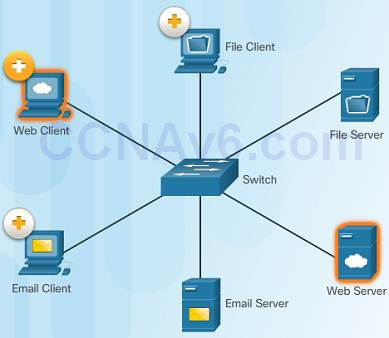
i.1.2.2 – Clients and Servers
Every reckoner connected to a network is called a host or stop device.
Servers are computers that provide information to stop devices on the network. For example, email servers, web servers, or file server
Clients are computers that send requests to the servers to retrieve information such as a web page from a web server or electronic mail from an email server.
ane.ane.2.three – Peer-to-Peer

Client and server software usually run on separate computers.
However, in small businesses or homes, it is typical for a client to also function as the server. These networks are chosen peer-to-peer networks.
Peer-to-peer networking advantages: easy to set up, less complex, and lower toll.
Disadvantages: no centralized administration, not equally secure, not scalable, and slower performance.
1.2 LANs, WANs, and the Cyberspace
one.2.1 – Network Components
one.two.1.i – Overview of Network Components
A network tin can exist as simple equally a single cablevision connecting two computers or as circuitous as a collection of networks that bridge the world.
Network infrastructure contains three broad categories of network components:
♦ Devices
♦ Media
♦ Services
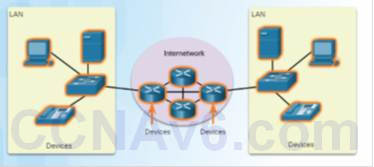
one.2.1.2 – Terminate Devices
An end device is where a message originates from or where it is received.
Data originates with an end device, flows through the network, and arrives at an end device
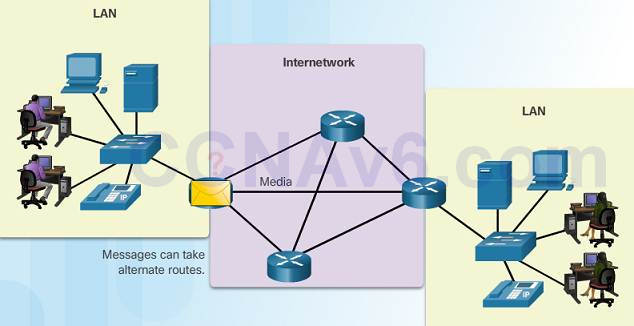
i.2.1.3 – Intermediary Network Devices
An intermediary device interconnects end devices in a network. Examples include: switches, wireless access points, routers, and firewalls.
The management of information as it flows through a network is likewise the role of an intermediary device including:
♦ Regenerate and retransmit information signals.
♦ Maintain information about what pathways exist through the network and internetwork.
♦ Notify other devices of errors and advice failures.

i.two.1.4 – Network Media
Advice across a network is carried through a medium which allows a message to travel from source to destination.
Networks typically use three types of media:
♦ Metallic wires inside cables, such as copper
♦ Glass, such as fiber optic cables
♦ Wireless transmission

ane.2.1.5 – Network Representations
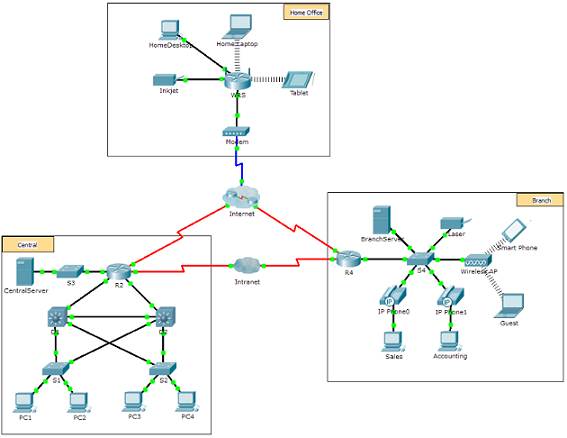
Network diagrams, frequently chosen topology diagrams, apply symbols to stand for devices within the network.
In addition to the device representations on the right, it is important to remember and understand the following terms:
♦ Network Interface Bill of fare (NIC)
♦ Physical Port
♦ Interface
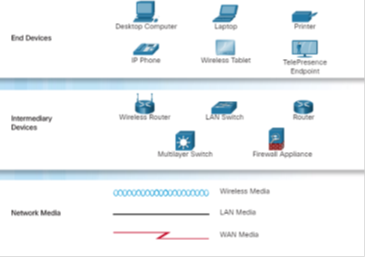
1.2.1.half-dozen – Topology Diagrams
Annotation the key differences between the two topology diagrams (physical location of devices vs. ports and network addressing schemes)
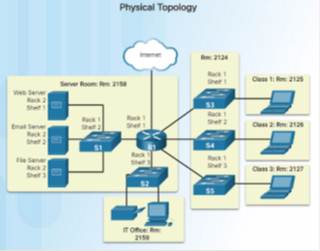
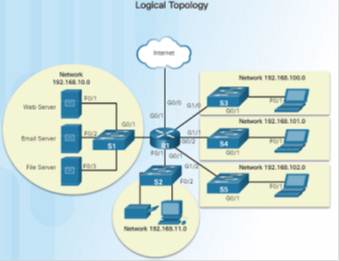
1.two.ii – LANs and WANs
i.two.2.1 – Types of Networks
Two nigh common types of networks:
♦ Local Area Network (LAN) – spans a small geographic area owned or operated by an individual or Information technology section.
♦ Wide Expanse Network (WAN) – spans a large geographic surface area typically involving a telecommunication service provider.
♦ Other types of networks:
♦ Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
♦ Wireless LAN (WLAN)
♦ Storage Area Network (SAN)
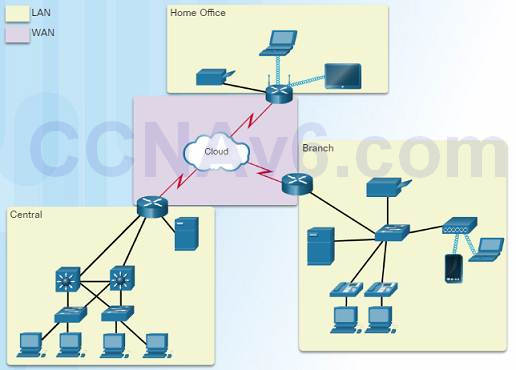
1.ii.two.2 – Local Expanse Networks
Iii characteristics of LANs:
♦ Spans a small-scale geographic expanse such every bit a dwelling house, school, office building, or campus.
♦ Commonly administered by a unmarried organization or private.
♦ Provides high speed bandwidth to stop and intermediary devices within the network.
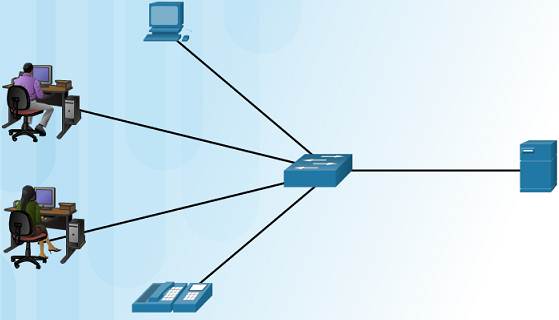
1.2.2.iii – Broad Surface area Networks
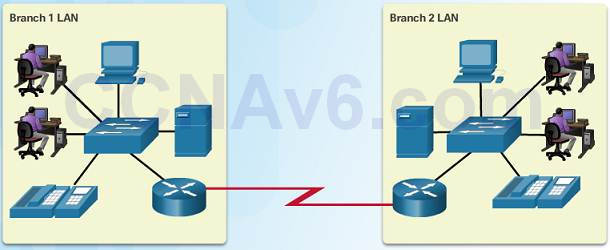
Three characteristics of WANs:
♦ WANs interconnect LANs over wide geographical areas such equally between cities, states, or countries.
♦ Usually administered by multiple service providers.
♦ WANs typically provide slower speed links between LANs.
i.2.3 – The Cyberspace, Intranets, and Extranets
i.2.three.1 – The Internet
The Internet is a worldwide collection of interconnected LANs and WANs.
LANs are continued to each other using WANs.
WANs are and then connected to each other using copper wires, fiber optic cables, and wireless transmissions.
The Cyberspace is non owned by any individual or group, however, the following groups were developed to assistance maintain structure:
♦ IETF
♦ ICANN
♦ IAB
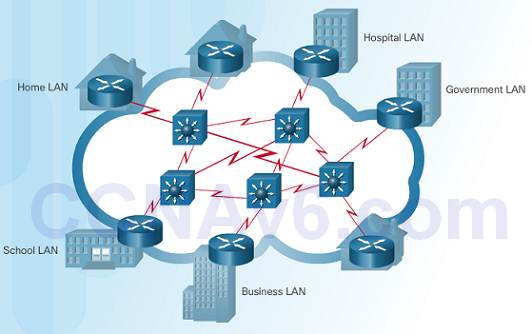
1.ii.iii.2 – Intranets and Extranets
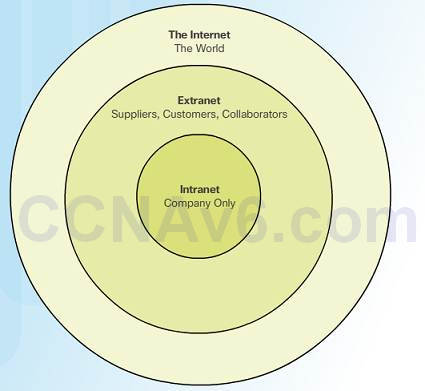
Unlike the Cyberspace, an intranet is a private collection of LANs and WANs internal to an organisation that is meant to be accessible just to the organizations members or others with authorisation.
An organization might use an extranet to provide secure admission to their network for individuals who work for a different organization that need admission to their data on their network.
ane.2.iv – Internet Connections
1.ii.4.1 – Internet Admission Technologies

There are many ways to connect users and organizations to the Internet:
♦ Popular services for abode users and small offices include broadband cable, broadband digital subscriber line (DSL), wireless WANs, and mobile services.
♦ Organizations need faster connections to back up IP phones, video conferencing and data center storage.
♦ Business-class interconnections are unremarkably provided by service providers (SP) and may include: business DSL, leased lines, and Metro Ethernet.
1.2.4.2 – Dwelling and Small Office Internet Connections
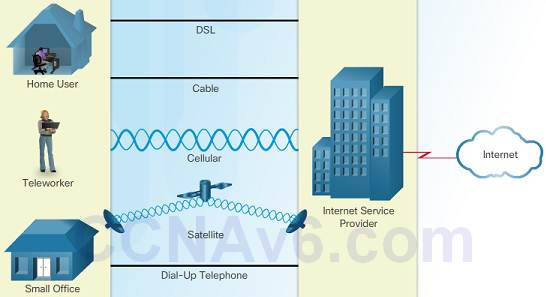
Cable – high bandwidth, e'er on, Internet connection offered by cable television service providers.
DSL – high bandwidth, e'er on, Internet connection that runs over a telephone line.
Cellular – uses a jail cell phone network to connect to the Internet; only available where y'all can get a cellular signal.
Satellite – major do good to rural areas without Cyberspace Service Providers.
Dial-up phone – an inexpensive, low bandwidth option using a modem.
ane.2.4.3 – Businesses Internet Connections
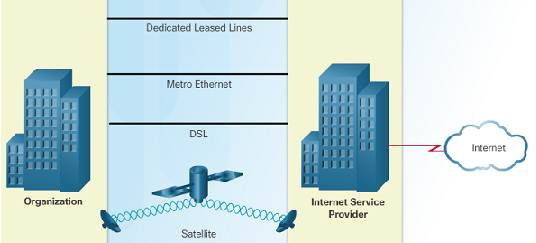
Corporate business connections may require higher bandwidth, dedicated connections, or managed services. Typical connection options for businesses:
♦ Defended Leased Line – reserved circuits inside the service provider's network that connect afar offices with private vocalization and/or data networking.
♦ Ethernet WAN – extends LAN admission technology into the WAN.
♦ DSL – Business DSL is available in various formats including Symmetric Digital Subscriber Lines (SDSL).
♦ Satellite – can provide a connectedness when a wired solution is not available.
1.ii.4.four – Bundle Tracer – Help and Navigation Tips
♦ Overview of the Packet Tracer Program
♦ Packet Tracer is a fun software program which will help you lot with your CCNA studies by allowing you to experiment with network behavior, build networks, and find the answers to your "what if" questions.
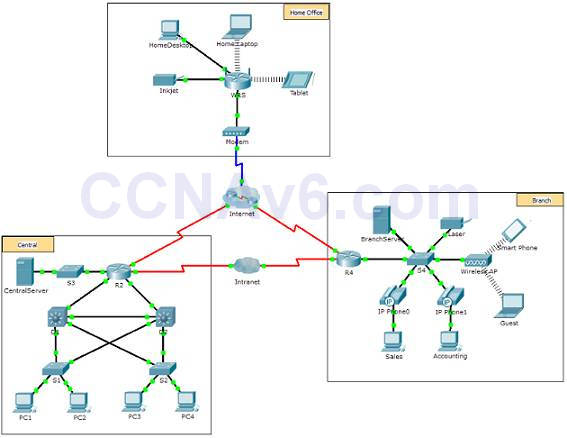
1.2.4.five – Bundle Tracer – Network Representation
This activity volition allow you to explore how Bundle Tracer serves as a modeling tool for network representations.
The network model in this action incorporates many of the technologies you lot volition need to principal in your CCNA studies.
i.three – The Network every bit a Platform
1.3.1 – Converged Networks
ane.3.ane.one – Traditional Carve up Networks
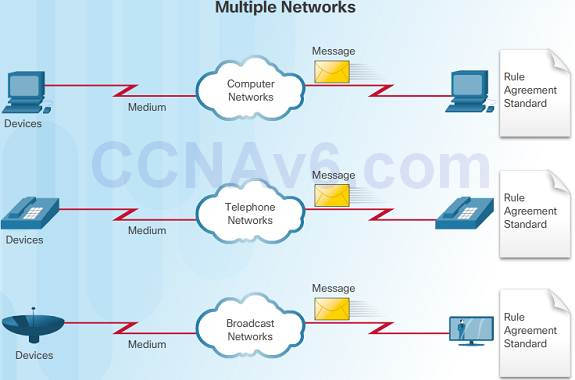
An case of multiple networks might exist a school 30 years ago. Some classrooms were cabled for data networks. Those aforementioned classrooms were cabled for telephone networks, and as well cabled separately for video.
Each of these networks used different technologies to carry the advice signals using a dissimilar set of rules and standards.
i.iii.1.2 – The Converging Network
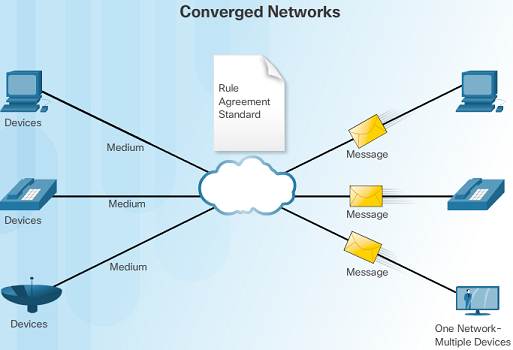
Converged information networks carry multiple services on one link including data, vox, and video.
Unlike dedicated networks, converged networks tin deliver data, voice, and video between different types of devices over the same network infrastructure.
The network infrastructure uses the same set of rules and standards.
i.3.ane.3 – Lab – Researching Converged Network Services

1.three.ii – Reliable Network
1.3.2.1 – Network Architecture
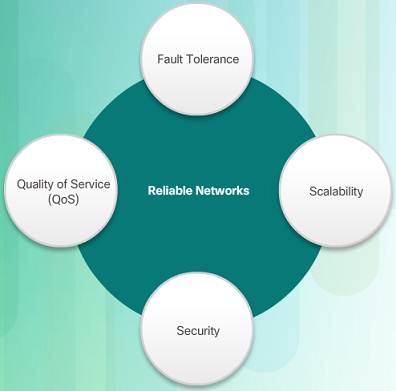
Network Compages refers to the technologies that support the infrastructure that moves data beyond the network.
There are four basic characteristics that the underlying architectures need to address to meet user expectations:
♦ Fault Tolerance
♦ Scalability
♦ Quality of Service (QoS)
♦ Security
1.3.2.2 – Fault Tolerance
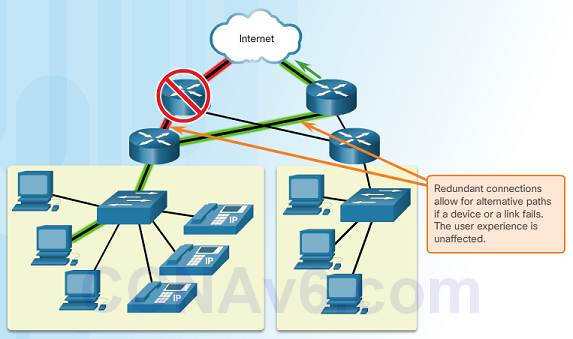
A fault tolerant network limits the touch on of a failure by limiting the number of affected devices.
Multiple paths are required for fault tolerance.
Reliable networks provide redundancy by implementing a bundle switched network. Bundle switching splits traffic into packets that are routed over a network. Each packet could theoretically take a different path to the destination.
This is not possible with circuit-switched networks which establish defended circuits.
1.iii.2.3 – Scalability
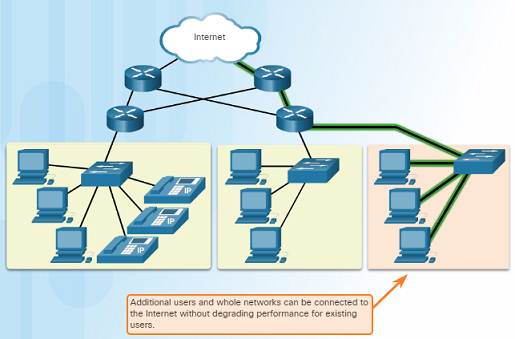
A scalable network can expand quickly and easily to back up new users and applications without impacting the performance of services to existing users.
Network designers follow accepted standards and protocols in social club to make the networks scalable.
1.three.2.4 – Quality of Service
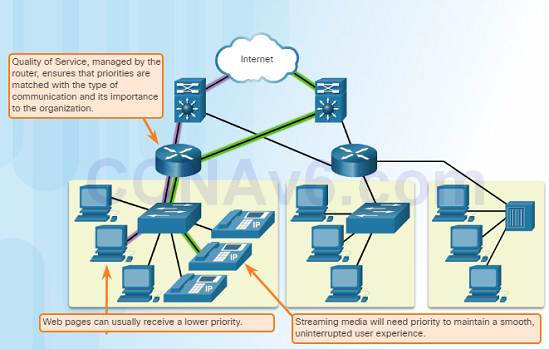
Vocalism and live video transmissions require college expectations for those services being delivered.
Have you ever watched a live video with abiding breaks and pauses? This is caused when in that location is a higher demand for bandwidth than available – and QoS isn't configured.
Quality of Service (QoS) is the primary mechanism used to ensure reliable delivery of content for all users.
With a QoS policy in place, the router can more easily manage the period of data and vocalization traffic.
one.3.2.5 – Security
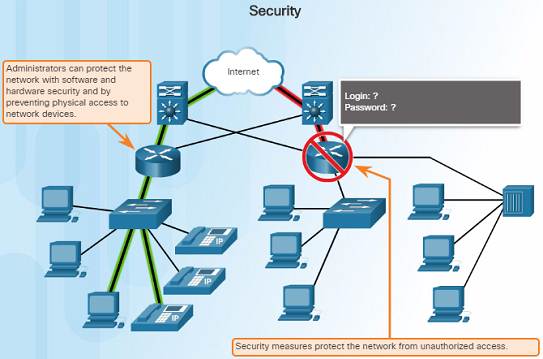
There are two master types of network security that must be addressed:
♦ Network infrastructure security
◊ Concrete security of network devices
◊ Preventing unauthorized admission to the direction software on those devices
♦ Information Security
◊ Protection of the information or information transmitted over the network
♦ Iii goals of network security:
◊ Confidentiality – only intended recipients tin read the data
◊ Integrity – assurance that the data has not be altered with during manual
◊ Availability – assurance of timely and reliable access to data for authorized users
1.4 – The Changing Network Environment
1.4.1 – Network Trends
1.4.1.1 – New Trends

The office of the network must arrange and continually transform in order to be able to keep up with new technologies and finish user devices as they constantly come to the market.
Several new networking trends that effect organizations and consumers:
♦ Bring Your Own Device (BYOD)
♦ Online collaboration
♦ Video communications
♦ Cloud computing
1.4.1.2 – Bring Your Own Device
Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) is a major global trend that allows users to utilise their own devices giving them more opportunities and greater flexibility.
BYOD allows end users to have the freedom to use personal tools to admission data and communicate using their:
♦ Laptops
♦ Netbooks
♦ Tablets
♦ Smartphones
♦ E-readers
i.four.one.3 – Online Collaboration
Individuals want to interact and piece of work with others over the network on joint projects.
Collaboration tools including Cisco WebEx (shown in the figure) gives users a fashion to instantly connect, interact and attain their objectives.
Collaboration is a very high priority for businesses and in education.
ane.iv.ane.4 – Video Communication
Cisco TelePresence powers the new fashion of working where everyone, everywhere, can exist more productive through confront to face collaboration.
Around the world each 24-hour interval, we transform organizations past transforming our client experiences.

1.iv.1.five – Cloud Calculating
Cloud calculating is a global trend that allows us to shop personal files or backup our data on servers over the Internet.
Applications such as word processing and photograph editing tin can also exist accessed using the Cloud.
Cloud computing also allows businesses to extend their capabilities on demand and delivered automatically to any device anywhere in the globe.
Cloud computing is made possible past data centers. Smaller companies that tin can't afford their own data centers, lease server and storage services from larger data heart organizations in the Deject.
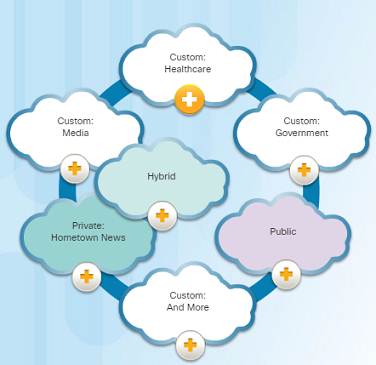
4 types of Clouds:
♦ Public Clouds
♦ Services and applications are fabricated available to the full general public through a pay-per-use model or for free.
♦ Private Clouds
♦ Applications and services are intended for a specific organization or entity such as the government.
♦ Hybrid Clouds
♦ Made upward of two or more Cloud types – for case, part custom and part public. Each part remains a distinctive object but both are connected using the same architecture.
♦ Custom Clouds
1.iv.ii – Network Trends
1.4.2.1 – Applied science Trends in the Home
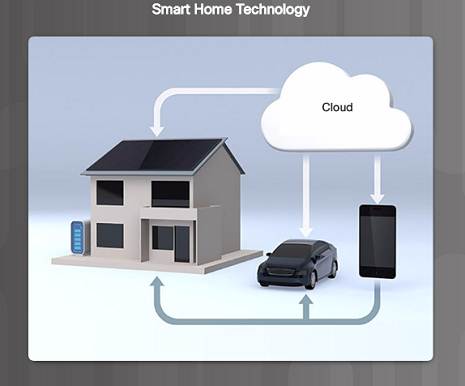
Smart home technology is a growing trend that allows technology to be integrated into every-day appliances which allows them to interconnect with other devices.
Ovens might know what fourth dimension to cook a repast for you lot by communicating with your calendar on what fourth dimension you are scheduled to exist dwelling house.
i.4.ii.2 – Powerline Networking
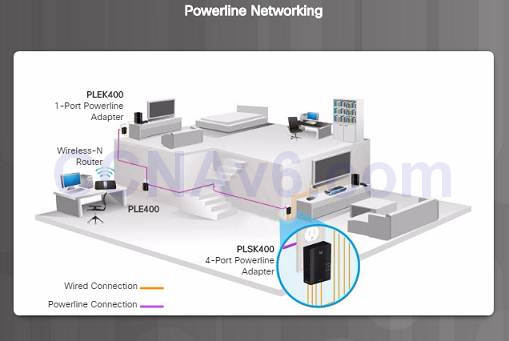
Powerline networking can allow devices to connect to a LAN where information network cables or wireless communications are not a viable option.
Using a standard powerline adapter, devices can connect to the LAN wherever there is an electrical outlet by sending data on certain frequencies.
1.4.ii.3 – Wireless Broadband

In addition to DSL and cable, wireless is another option used to connect homes and small businesses to the Cyberspace.
More commonly found in rural environments, a Wireless Internet service provider (WISP) is an Internet service provider that connects subscribers to designated access points or hotspots.
Wireless broadband is another solution for the dwelling house and modest businesses.
♦ Uses the same cellular technology used by a smart phone.
♦ An antenna is installed exterior the house providing wireless or wired connectivity for devices in the abode.
i.4.3 – Network Security
one.iv.3.1 – Security Threats
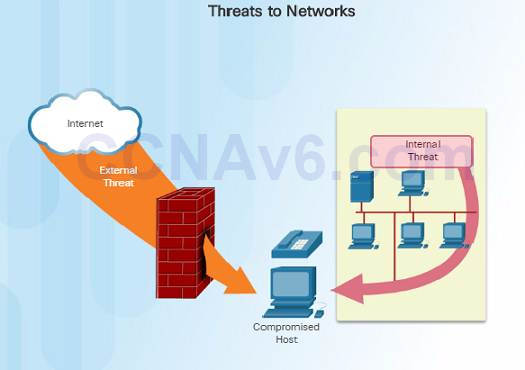
Network security is an integral role of networking regardless of the size of the network.
The network security that is implemented must accept into business relationship the environment while securing the data, but still allowing for quality of service that is expected of the network.
Securing a network involves many protocols, technologies, devices, tools, and techniques in order to secure data and mitigate threats.
Threat vectors might exist external or internal.
External threats:
♦ Viruses, worms, and Trojan horses
♦ Spyware and adware
♦ Zero-mean solar day attacks, likewise chosen aught-hr attacks
♦ Hacker attacks
♦ Denial of Service attacks
♦ Information interception and theft
♦ Place Theft
Internal threats:
♦ Whether intentional or not, many studies show that the internal users of the network crusade the virtually security breaches.
♦ With BYOD strategies, corporate information is more vulnerable.
ane.4.3.2 – Security Solutions
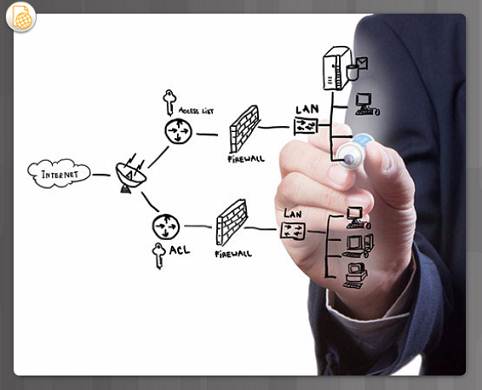
Security must be implemented in multiple layers using more than i security solution.
Network security components for dwelling house or small office network:
♦ Antivirus and antispyware software should be installed on stop devices.
♦ Firewall filtering used to block unauthorized admission to the network.
Larger networks have boosted security requirements:
♦ Dedicated firewall system to provide more advanced firewall capabilities.
♦ Access control lists (ACL) – used to further filter access and traffic forwarding.
♦ Intrusion prevention systems (IPS) – used to identify fast-spreading threats such every bit zero-day attacks.
♦ Virtual individual networks (VPN) – used to provide secure admission for remote workers.
1.iv.four – Network Architecture
1.4.4.1 – Cisco Network Compages

In guild for networks to function while efficiently supporting connections of people, devices, and information in a media rich converged surround, the network must be built upon a standard network compages.
Network architecture refers to the devices, connections, and products that are integrated to support the necessary technologies and applications.
The foundation of all network architectures including the Internet are routers and switches.
one.4.4.2 – CCENT and CCNA Certification
Cisco Certified Network Acquaintance (CCNA)
♦ Routing and Switching Certification
♦ Requires you to pass two exams:
♦ First exam: Cisco Certified Entry Network Technician (CCENT)
♦ Second test focuses on IPv4 and IPv6 routing and WAN technologies also as LAN switching and infrastructure services/maintenance
1.iv.4.iii – Lab – Researching Information technology and Networking Task Opportunities

1.5 Chapter Summary
1.5.1 – Conclusion
1.5.1.1 – Warriors of the Net
The animated video below volition help y'all visualize networking concepts.
http://world wide web.warriorsofthe.cyberspace/

1.5.one.ii – Exploring the Network

Networks and the Internet take dramatic impact on our lives.
A network can consist of two devices, or tin can be equally large as the Internet, consisting of millions of devices.
The network infrastructure is the platform that supports the network.
Networks must be:
♦ Fault tolerant
♦ Scalable
♦ Back up Quality of Service
♦ Secure
1.v.ii – Conclusion
ane.5.2.ane Affiliate i: Introduction to Networks
Explain how multiple networks are used in every day life.
Explicate how topologies and devices are continued in a small to medium-sized business network.
Explain the bones characteristics of a network that support communication in a small to medium-sized business organisation.
Explain trends in networking that volition bear upon the use of networks in pocket-sized to medium-sized businesses.
i.5.2.2 New Terms and Commands
| Peer-to-Peer File SharingSmall Office/Home Role or SOHO Medium to large network Server Customer Peer-to-Peer network End device Intermediary device Medium Network Interface Bill of fare (NIC) Physical Port Interface Physical topology diagram | Logical topology diagram Local Expanse Network (LAN) Broad Area Network (WAN) Cyberspace Intranet Extranet Internet access provider (Internet service provider) Converged networks Network architecture Fault tolerant network Packet-switched network Circuit-switched network Scalable network Quality of Service (Qos) | Network bandwidth Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) Collaboration Cloud computing Private clouds Hybrid clouds Public clouds Custom clouds Data center Smart home engineering science Powerline networking Wireless Isp (WISP) Network architecture |
Download Slide PowerPoint (pptx):
[sociallocker id="54558″]
[/sociallocker]
rossiforgerbours1990.blogspot.com
Source: https://itexamanswers.net/introduction-to-networks-6-0-instructor-materials-chapter-1-explore-the-network.html
Post a Comment for "Network+ Guide to Networks Review Questions Answers Chapter 1"